May 1, 2024
The Role of Hydraulic Piping in Heavy Machinery: A Comprehensive Overview

Team Pipe Processing
In the world of heavy machinery, hydraulic systems play an important role in ensuring smooth In the intricate and demanding world of heavy machinery, the role of hydraulic systems is fundamental. These systems, which harness the power of pressurized fluids to perform a myriad of tasks, are at the core of countless machines, driving their functionality with precision and force. Central to the efficacy of these hydraulic systems is their network of hydraulic piping; these are not merely channels, but the crucial arteries through which hydraulic fluid—a lifeblood of sorts—flows to empower various machine components.
The importance of hydraulic piping transcends mere function; it is integral to the very performance and reliability of heavy machinery. As the primary conduit for transmitting power, controlling pressure, and enabling the activation of hydraulic actuators, the integrity and efficiency of hydraulic piping systems are indispensable. A failure in this network can lead to a cascade of operational inefficiencies, jeopardizing the machinery's performance and safety.
This comprehensive overview seeks to unpack the multiple facets of hydraulic piping within heavy machinery. We will explore the key functions of hydraulic piping, delve into the various types available and the criteria for selecting them, and discuss essential maintenance practices to uphold their operation.
Additionally, we will look ahead to the emerging trends and innovations shaping the future of hydraulic piping. Understanding these elements is crucial for any stakeholder in the industry aiming to enhance the longevity and efficiency of their machinery, ensuring robust performance in demanding environments.
Wikipedia: Hydraulic Machinery
Understanding Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic systems are a cornerstone of modern heavy machinery, leveraging the principles of fluid dynamics to perform powerful and controlled tasks. These systems are composed of several key components: hydraulic pumps that create flow, actuators that convert hydraulic energy into mechanical motion, valves that control the flow and direction of the fluid, and, vitally, the hydraulic piping that connects them all. The hydraulic fluid, typically a type of oil, is pressurized by the system's pumps. This pressurization enables it to transmit force across the system, activating various mechanical components such as cylinders, motors, and valves, each integral to the machinery's operation.
Importance of Hydraulic Piping in Heavy machinery
Acting much like the circulatory system in a living organism, hydraulic piping is essential for the health and efficiency of hydraulic systems. It ensures the seamless transport of pressurized hydraulic fluid to various parts of the machinery, fulfilling several critical roles: it transmits mechanical power, manages system pressure to optimize performance, and facilitates the precise movements of hydraulic actuators. The efficiency of a hydraulic system is deeply contingent upon the integrity and design of its piping; inadequate or faulty piping can lead to reduced machine performance, operational inefficiencies, and even system failures. Such shortcomings underscore the piping's pivotal role in maintaining the robustness and reliability of hydraulic systems.
Types of Hydraulic Pipes
Hydraulic pipes come in various materials, including steel, stainless steel, and rubber, each suited to different applications based on factors such as pressure requirements, environmental conditions, and fluid compatibility Selecting the appropriate type of pipe is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the hydraulic s.stem. Key factors influencing pipe selection include pressure requirements, environmental conditions, and compatibility with the hydraulic fluid. Let's delve into the most common types of hydraulic pipes:
Steel Pipes:
Reigning supreme in high-pressure applications are seamless steel pipes. Forged from a solid piece of steel, these pipes boast exceptional strength and resistance to bursting. They are the go-to choice for heavy-duty machinery like excavators and industrial presses due to their unparalleled durability. A more cost-effective alternative is welded steel pipes. Sections of steel are joined together to create a strong and reliable pipe. However, the weld acts as a potential weak spot, so pressure limitations need to be considered. Welded steel pipes find favor in moderate pressure applications within construction equipment and agricultural machinery.
Important considerations for steel pipes include weight: steel adds significant weight to the machinery. Additionally, steel is susceptible to rust, especially in environments with moisture or salt. Opt for galvanized or stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance. Finally, steel pipes require specialized equipment and expertise for cutting, bending, and welding.
Stainless Steel Pipes:
When battling corrosion, stainless steel pipes emerge victorious. Their exceptional corrosion resistance ensures reliable performance and a longer lifespan in environments with salt water, harsh chemicals, or extreme temperatures. They are commonly seen in marine equipment, chemical processing plants, and food production facilities.
Considerations for stainless steel pipes include cost: stainless steel is a pricier option compared to regular steel. They also share the weight concern of regular steel pipes, adding significant weight to the machinery.
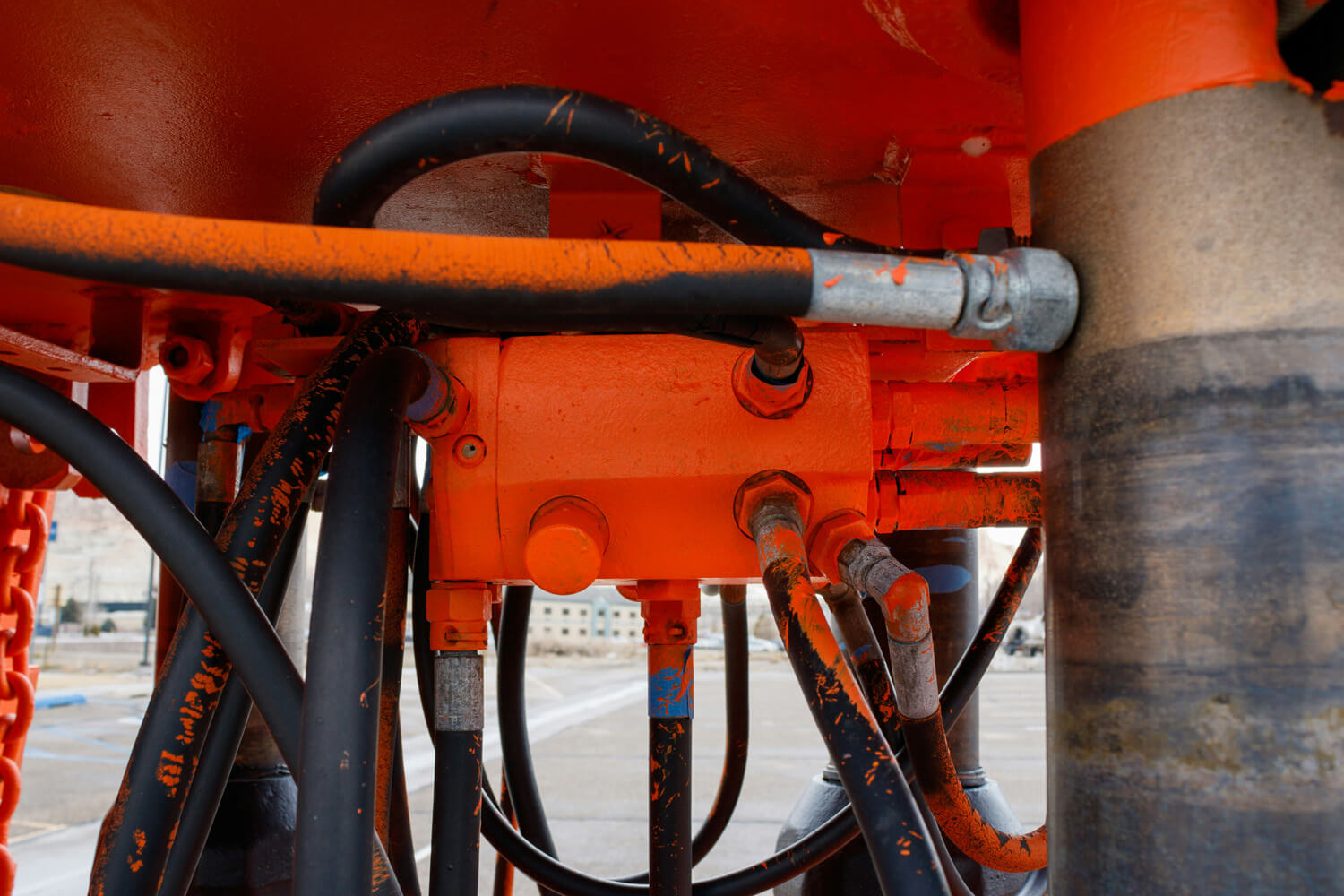
Hydraulic Hoses:
For applications demanding flexibility, hydraulic hoses are the undisputed champions. Typically constructed from high-pressure synthetic rubber with steel wire or braid reinforcements, these hoses excel at bending and navigating tight spaces where rigid pipes would be impractical. They are ideal for applications requiring movement, such as on backhoe arms or robotic arms in factories.
However, hydraulic hoses come with their own considerations:
Their pressure limitations mean they cannot handle the same extreme pressures as steel pipes. The pressure rating of the hose needs to be carefully matched to the application.
Hoses are also more prone to punctures or abrasions compared to steel pipes, so proper routing and protection are crucial to ensure their longevity. Finally, some hose materials are sensitive to temperature extremes, so choosing the right hose material for the operating temperature range is essential.

Beyond these main categories, there are also specialized hydraulic pipes for specific needs:
Thermoplastic hoses:
A lightweight and cost-effective option for low-pressure applications where weight is a concern.
High-pressure thermoplastic hoses:
Advancements in material science have led to the development of high-pressure thermoplastic hoses that offer an alternative to steel pipes in certain applications.
Biodegradable hoses:
Environmentally conscious options are becoming available, made from materials that decompose naturally after their lifespan.
By understanding the strengths and considerations of each type of hydraulic pipe, you can select the most suitable option for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity of your hydraulic system.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Hydraulic Piping
Regular maintenance is paramount to ensure the reliability and performance of hydraulic piping systems. This includes periodic inspections, leak detection, and replacement of worn-out components. Common issues with hydraulic piping include leaks, corrosion, and blockages, which can be addressed through proper maintenance procedures and troubleshooting techniques. Timely detection and resolution of these issues are crucial to prevent costly downtime and repairs.
Innovations in Hydraulic Piping Technology
The world of hydraulic piping is no stranger to innovation. Driven by advancements in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and fluid dynamics, the future of hydraulics is brimming with exciting possibilities. Let's explore some of the key areas where innovation is transforming the landscape:
Lightweight Champions:
Traditional steel pipes, while incredibly strong, can add significant weight to machinery. New research focuses on developing lighter yet robust materials like composite pipes that combine the strength of fibers like carbon fiber with the flexibility of polymers. This translates to lighter, more fuel-efficient machinery.
Sealing the Deal:
Leak-Free Performance: Even the smallest leak in a hydraulic system can lead to significant problems. Improved sealing mechanisms are being developed, such as innovative crimping methods and advanced gasket materials. These advancements not only minimize leaks but also simplify and expedite assembly processes.
The Doctor is In:
Diagnostic Tools for Peak Performance Just like a Formula One race car, modern hydraulic systems are getting smarter. The integration of sensors throughout the piping network allows for real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and flow rates. This data can be fed into advanced diagnostic tools that can predict potential issues before they occur, allowing for preventative maintenance and avoiding costly downtime.
The Internet of Hydraulics:
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is making its way into hydraulic systems as well. Imagine embedding tiny sensors directly into hydraulic pipes that can wirelessly transmit data to a central hub. This data can be used for real-time performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and even remote troubleshooting. This not only improves efficiency but also opens doors for new service models and preventative maintenance strategies.
Biodegradable Solutions for a Sustainable Future:
Environmental consciousness is at the forefront of many industries, and hydraulic piping is no exception. Research is underway to develop biodegradable hydraulic hoses made from sustainable materials that decompose naturally after their lifespan. This not only reduces environmental impact but also eliminates the need for disposal of traditional non-biodegradable hoses.
Conclusion
Hydraulic piping plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of heavy machinery. Understanding its functions, types, maintenance requirements, and future trends is essential for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of hydraulic systems. By investing in quality piping materials, adopting proactive maintenance practices, and embracing technological innovations, businesses can ensure the seamless operation of their hydraulic machinery, driving productivity and competitiveness in today's dynamic industrial landscape.
Ready to enhance your hydraulic systems? Contact us today for expert advice and customized solutions to keep your machinery running at peak performance.
Related Blog: Hydraulic Piping: Fundamentals, Types, and Significance
Share it!
PIPE PROCESSING TECHNICAL INSTITUTE
Streamline Your Pipe Processing Challenges
Streamline Your Pipe Processing Challenges
Struggling with customization complexity, tight deadlines, or rising costs? We deliver:
- Precision bending for custom designs
- Fast turnarounds for tight schedules
- Cost-effective solutions for any scale
Partner with Pipe Processing Technical Institute to streamline your production and overcome challenges with ease.